Blockchain for Data Provenance
November 2, 2021
Blockchain for Networked Device Identity Management
November 2, 2021
Problem
There is a lack of tools or technologies that can protect the entire cyber supply chain and ensure that all software and firmware verified for their trustworthiness before they are integrated into EDS OT. We will develop permissioned blockchain based data provenance techniques to certify the software and firmware at all stages of an cyber supply chain in EDS so that the end-users can easily verify whether the purchased electronic component’s software or firmware is tampered with or not. We will develop integrity mechanisms for permissioned blockchain platforms so that critical data remains secure even in the presence of data breach attacks.
Approach
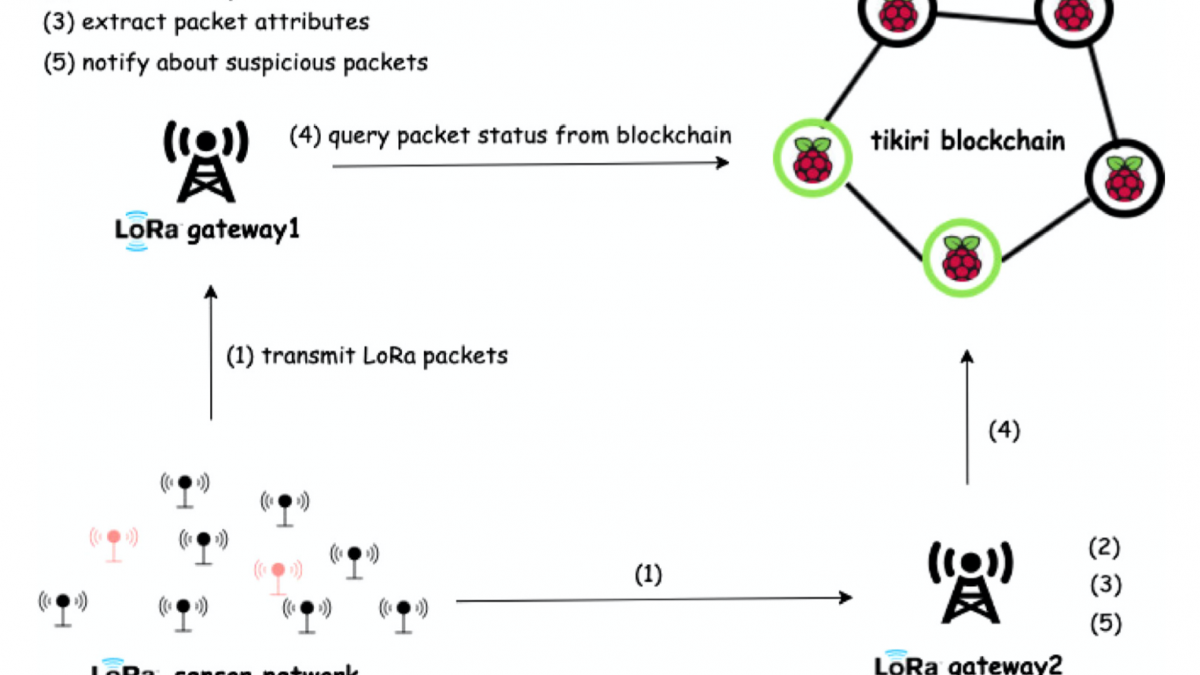
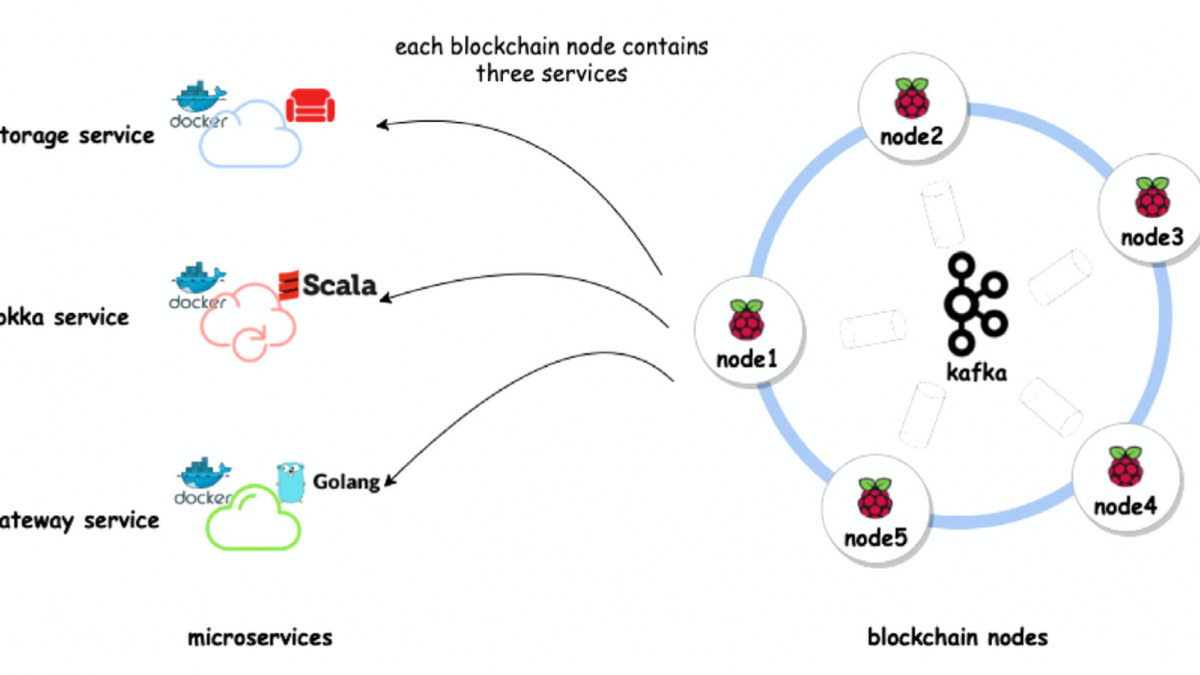
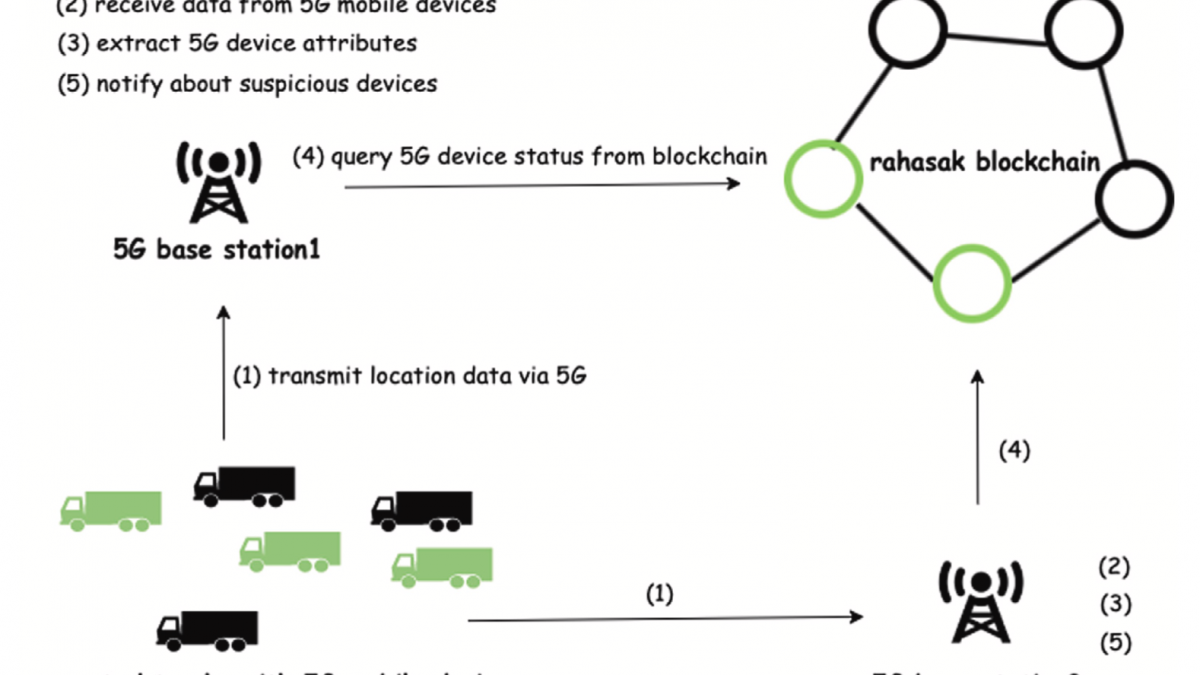
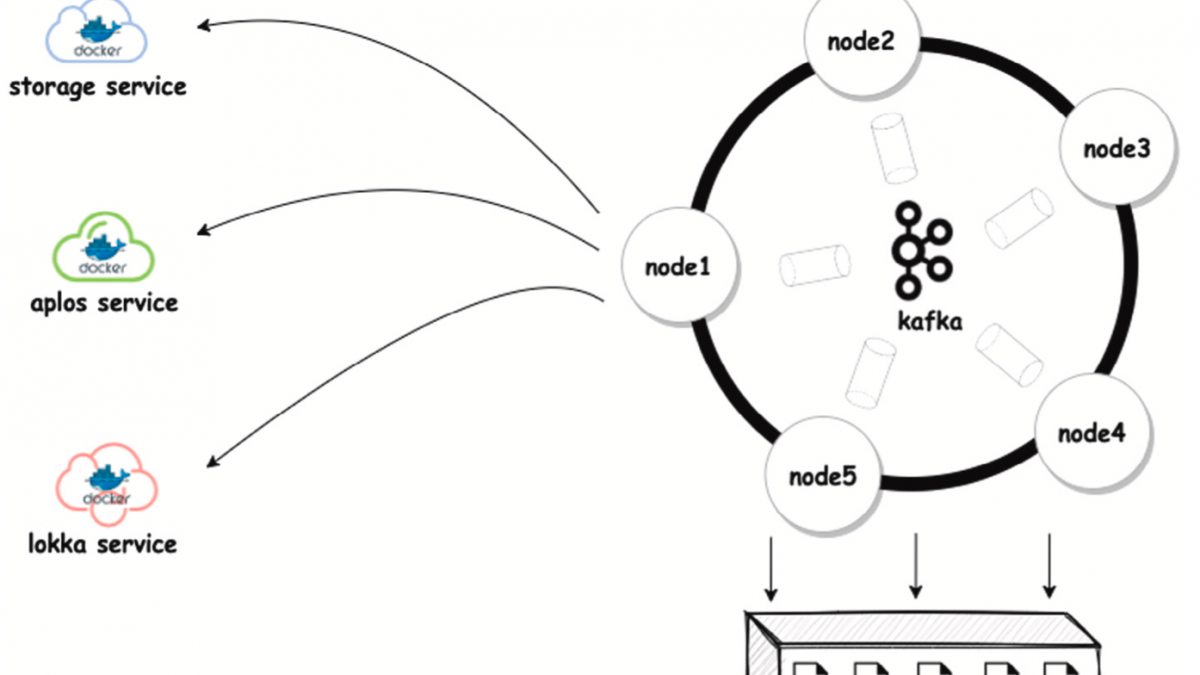
The approach proposed in this activity focuses on customized consensus engine for cyber supply chain provenance and security mechanisms in permissioned blockchain platforms. We will develop a customized consensus engine which will not require participants in the cyber supply chain to make significant investment on computation and will balance the tradeoff between number of transactions processed, transaction validation time, incentives and security rules set by participators in the cyber supply chain. We will develop a capability for encoding the electronic component’s firmware/software design into transactions while balancing tradeoff between validation accuracy and latency. We will develop strategies to encode the firmware/software design and their computed hash values will be encoded in the blockchain. The hash values and the firmware/software designs will be delivered through the cyber supply chain and participators at every stage can ensure authenticity of the design by verifying the hash values. However, allocation of appropriate incentives for the participants is another emerging challenge where the trade-off between the incentive and cost of participation in consensus needs to be resolved. We will develop game theoretic based incentive mechanism to self-motivate participators in order to participate in the consensus. We will develop a layer for security assurance within the blockchain architecture to protect the business critical data. Data and transactions will be encrypted using threshold cryptography, such that multiple validating nodes must interact in order to decrypt and compute over this data. This will ensure that business critical data is not revealed even in the event that some number of the validating nodes are compromised.
Accomplishment
The team has developed an open source software tool (CyScPro).
Publications
- Xueping Liang, Sachin Shetty, Deepak Tosh, Yafei Ji, Danyi Li, “Towards a Reliable and Accountable Cyber Supply Chain in Energy Delivery System using Blockchain”, 14th EAI International Conference on Security and Privacy in Communication Networks (SecureComm), August 2018 (Acceptance ratio: 30.5%=33/108)
- Eranga Herath, Xueping Liang, Sachin Shetty,Pete Foytik, "Rahasak - Scalable Blockchain Architecture for Enterprise Applications," Journal of Systems Architecture (Accepted) 2021
- Eranga Herath, Xueping Liang, Pete Foytik, Sachin Shetty,"Promize - Blockchain and Self Sovereign Identity Empowered Mobile ATM Platform," SAI Computing Conference(Accepted) , 2021.
- Eranga Herath, Xueping Liang, Pete Foytik, Sachin Shetty, Nalin Ranasinghe,Kasun De Zoysa,Wee Keong Ng, "SaaS - Microservices-Based Scalable Smart Contract Architecture," SSCC 2020. Communications in Computer and Information Science, vol 1364. Springer, Singapore.
- S. P. Gochhayat, Sachin Shetty, R. Mukkamala, P. Foytik, G. A. Kamhoua and L. Njilla, "Measuring Decentrality in Blockchain Based Systems," in IEEE Access, vol. 8, pp. 178372-178390, 2020.
- Eranga Bandara, Xueping Liang, Sachin Shetty, Wee Keong Ng, Peter Foytik, Nalin Ranasinghe, Kasun De Zoysa, Bård Langöy, David Larsson, "Lekana - Blockchain Based Archive Storage for Large-Scale Cloud Systems," ICBC 2020.
- Eranga Bandara, Xueping Liang, Peter Foytik, Sachin Shetty, Nalin Ranasinghe, Kasun De Zoysa, "Bassa-Scalable Blockchain Architecture for Smart Cities," ISC2 2020.
- Xueping Liang, Sachin Shetty, "A State-aware Proof of Stake Consensus Protocol for Power System Resilience," In Proceedings of the Tenth ACM International Conference on Future Energy Systems, 2019, New York, NY, USA